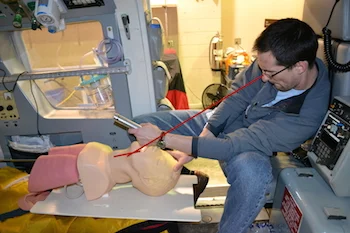
Video Laryngoscopy in the Field? Absolutely
/Close your eyes... actually open them up, you won't be able to read the description if you close your eyes... Imagine you are on flying on the helicopter for a scene flight. You land and are brought to the patient, a victim of a motorcycle accident who is clearly in need of an airway. He is obtunded with sonorous respirations, a GCS of 6, O2 sats in the low 90's. You start to look and assess the patient's airway and you are decidedly less than pleased.
Read More